Moving the robot
Slides
F for fullscreen · O for overview
Motor connection
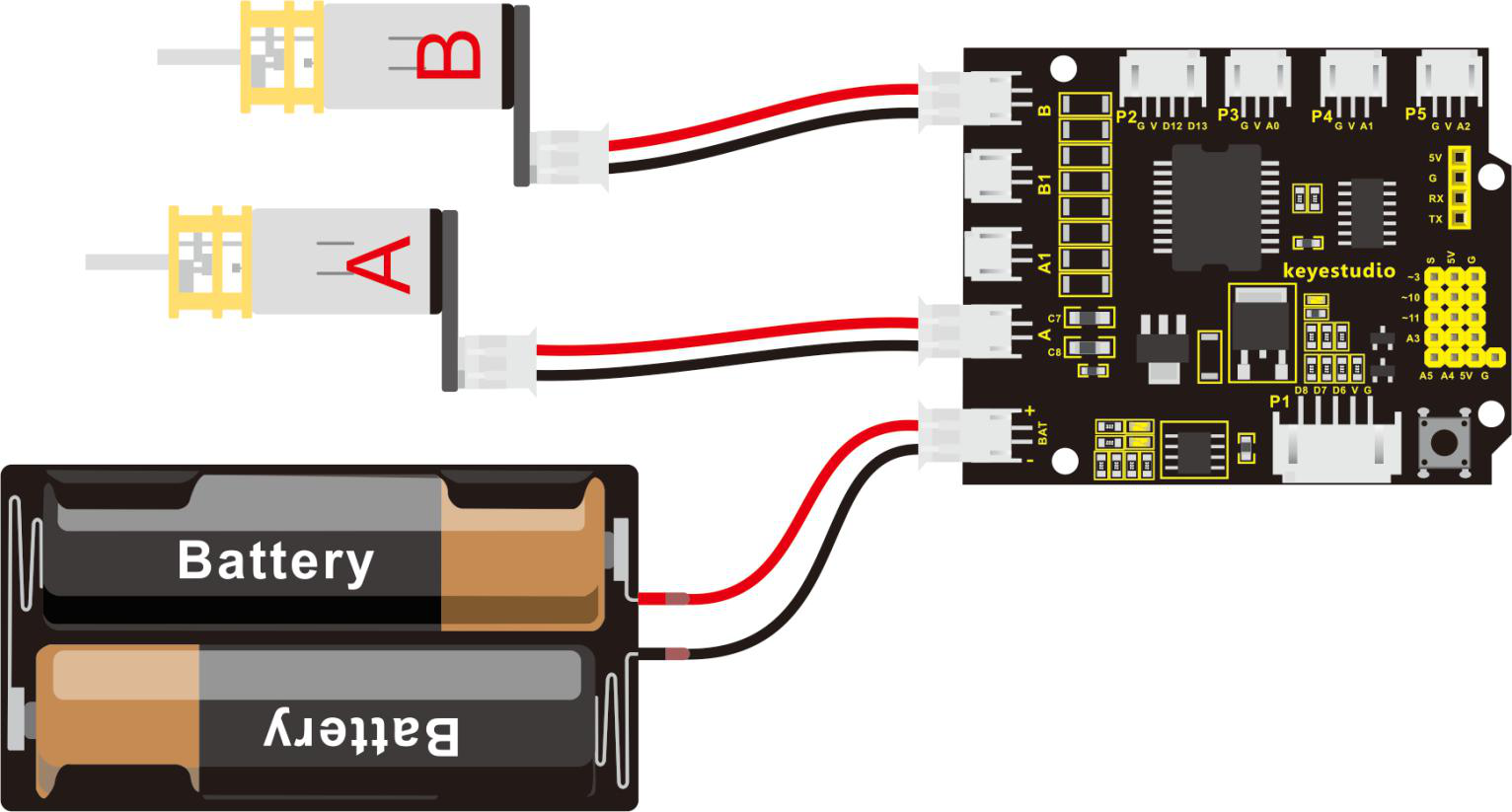
Control motor
In controlling a motor, we are controlling the speed and direction of the motor. A motor can move at different speeds at either forward or backward direction.
The speed and direction of the motors are controlled by the following pins
| Motor | Parameter | Pin |
|---|---|---|
| A | speed | 9 |
| direction | 2 | |
| B | speed | 5 |
| direction | 4 |
As we are controlling the motor by sending signal through the pins SA, SB, DA, DB, we need to set them as output.
To set motor A to move forward with roughly half speed, we can use
-
Control direction of a motor
pinis the pin number of the motor directionlevelis eitherHIGH(forward) orLOW(backward) to denote the direction of the motor
-
Control speed of a motor
pinis the pin number of the motor speedvalueis a numerical value from 0 (stop) to 255 (full speed) to control the speed of the motor
We normally set the direction before setting the speed. This is to avoid the motor moving in unexpected direction when we give the speed.
Moving forward
Moving backward
The robot can be moved backward easily by changing the direction of the motors from HIGH to LOW
Combining forward and backward
As moving forward and backward are common actions for robot, we would create functions that we can call easily whenever we need them.
After we have the moveForward and moveBackward functions, if we need the robot to move forward for 1 second and then move backward for 1 second, and repeat this process, we can
Bring it further
- How do we stop the robot from moving?
- How do we turn left or right?